March 12 is Equal Pay Day – which represents the date into the year women must work in order to earn the same amount as the average man the previous year. But what does that mean? And what can we say about the gender wage gap today?
Here are five fast facts:
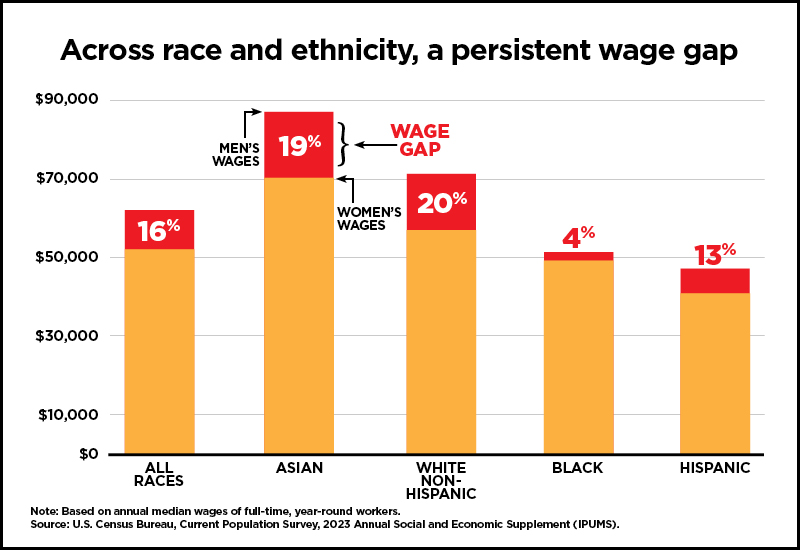
- Overall, women are paid less than men. On average, women working full-time, year-round are paid 84% of what men are paid. In other words, the typical woman working full-time would need to work from January 1, 2023, until March 12, 2024, to make what the typical man working full-time made in 2023. This wage gap also persists within all major race and ethnic groups. For instance, Hispanic women ($41,137 median annual salary) make 13% less than Hispanic men ($47,420 median annual salary). This inequity is even greater for Black and Hispanic women when compared to white, non-Hispanic men.
- The largest identifiable causes of the gender wage gap are differences in the occupations and industries where women and men are most likely to work. In 2023, Black women lost $42.7 billion and Hispanic women lost $53.3 billion in wages as compared to white men due to the impact of occupational segregation. However, even within the same occupation, women make less on average than men.
View our new fact sheet on lost wages due to occupational segregation for Black and Hispanic women.
- A woman must complete at least one additional educational degree to earn as much as a man with less education. For instance, on average, a woman with an advanced degree earns less than a man with a bachelor’s degree. Were it not for the fact that women attain a greater number of degrees than men, the gender wage gap would be even larger.
- The wage gap is larger for mothers and results in employment-related losses of more than $295,000 over a lifetime. This results in women having lower average incomes in retirement and less financial stability in old age.
- Discrimination remains a likely leading cause of the gender wage gap. Just since Fiscal Year 2022, the Department of Labor’s Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission and the Department of Justice have collectively recovered over $20 million in monetary relief for women who have experienced pay discrimination in the workplace.
Erin George is an Economist at the Women’s Bureau. Gretchen Livingston is a Survey Statistician at the Women’s Bureau.
 U.S. Department of Labor Blog
U.S. Department of Labor Blog